Project genesis
Real Estate is a well-established industry, complex, and a huge challenge at a young age (article of US millennials). Trying to change it is not the goal, so it all comes down to upgrading real estate.
Real Estate weaknesses are blockchain’s strengths
The project: Become an owner easily

My journey starts back in September 2021, I met Jean-Charles Baptista at the International Blockchain Stampede 2021. He suggested integrating blockchain into real estate.
The team consisted first of Jean-Charles Baptista, Ph.D. colleague Cyril Naves and myself.
The concept isn’t new, since the birth of Bitcoin and its early adoption, investors and buyers have tried and succeeded in using cryptocurrencies as a payment method (and more recently a Miami Penthouse). There is an increase in demand for secure, automated, and accelerated processes. The key element to a successful business is trust. As explained by this 2019 IBM article, real estate agents provide the trust from start to end of any real estate transaction.
Blockchain provides trust without a third party. A nice graphical explanation of blockchain by Reuters Graphics here.
Existing Real Estate analysis and use cases
- Consensys: A fast and detailed analysis of blockchain benefits in real estate.
- Realt.co: Fractional and frictionless real estate investing using Ethereum public blockchain and decentralized trading (Uniswap). Currently mainly available in Detroit, Michigan and Chicago, Illinois. Investment starts from ~$50.
- Bricks.co: Real estate investment from 10€ (no blockchain used). Currently only available in France.
- Sapeb-valorcim.fr: First real estate promoter in France and Europe to exercise ownership rights over an entire building sold via blockchain.
- Articles: Forbes 2021, Forbes 2022, Reuters 2018
Hackathon’s project goal
The main goal is to explore and implement a blockchain solution to facilitate real estate transactions while following legal regulations. Indeed, it is the regulations that offer a legal framework. We do not change the current way things work, the goal is to facilitate the purchase, investment, and return of owners and tenants.
Ease real estate transactions, using distributed ledger technology.
Hackathon’s project PoC implementation
The technology
The Substrate Framework is a perfect fit for developing a Proof of Concept. It has a very modular structure, good templates, and good documentation.
The team

Marketing & Economics

Real Estate Credit & Banking Strategy

Investment & Regulation

Cloud and Hosting (Ziosting)
Draft implementation
We called our first implementation UpDownStreet. Available at https://www.updownstreet.com/.
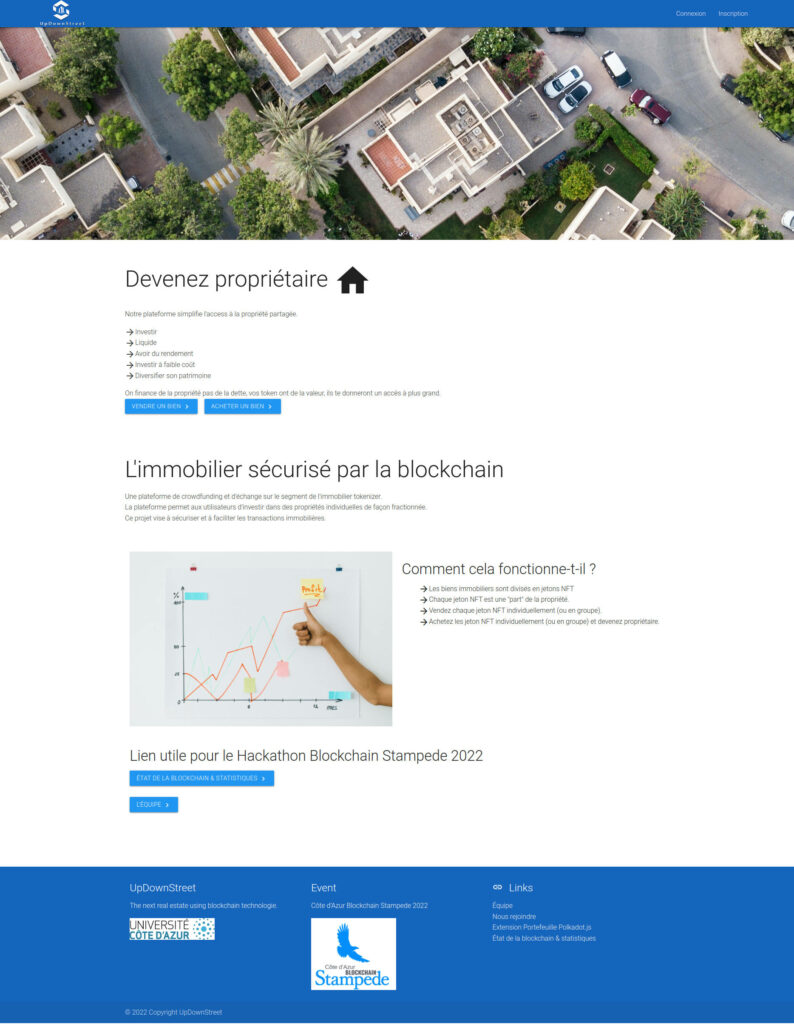
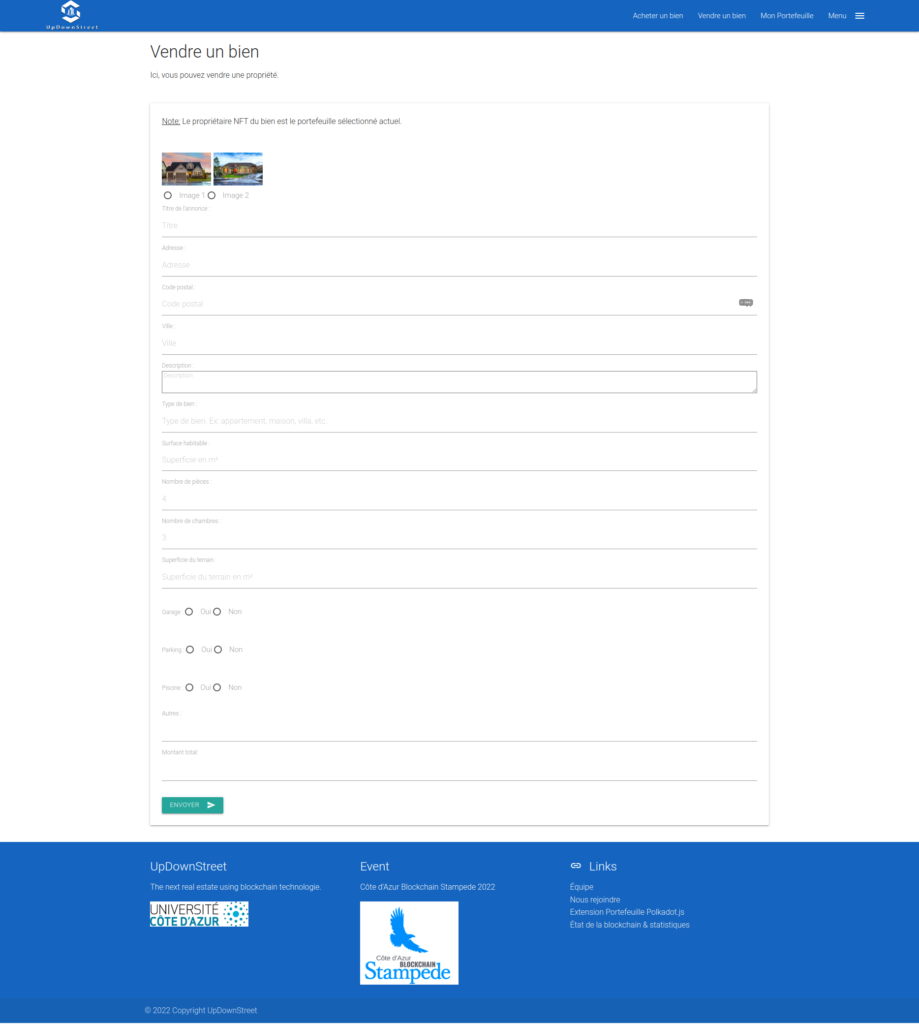
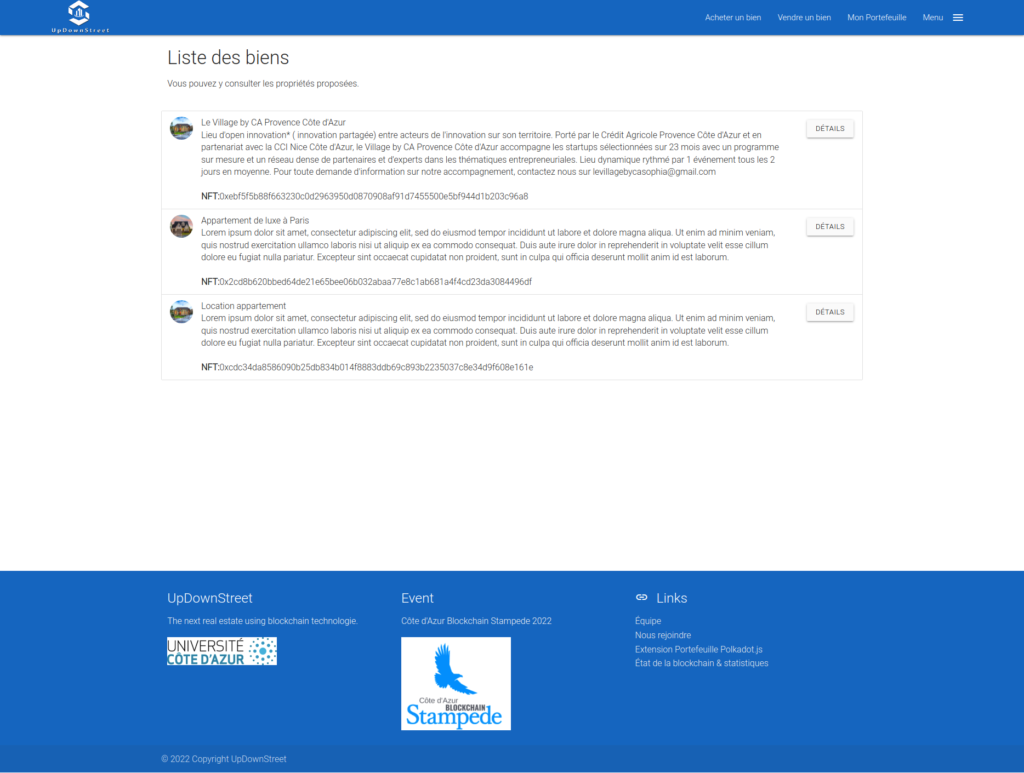
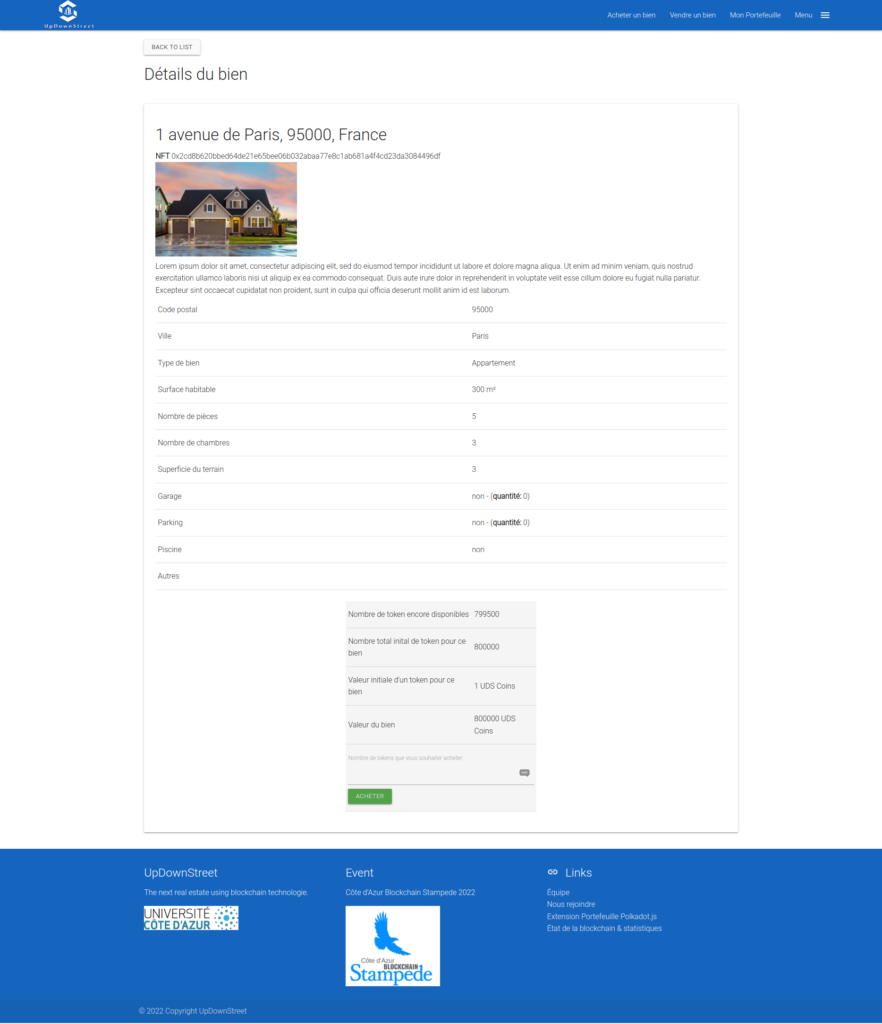
The PoC is here to have an overview of the final solution. It shows how easy it would be to become an owner and to sell a property.
The PoC demo has a real blockchain behind the scene with a Substrate module (aka smart contract) handling the NFTs. We opt for a private blockchain.
Why a private blockchain?
Government regulation requires the company behind the project to have special rights, thus special access, management of the contracts and database. This means there is not full immutability but the blockchain allows full transparency to all users and governmental regulators. Also, private blockchain has no transaction fees and has a fast transaction execution rate.
The PoC demo features are:
- Register & login
- Sell a property (create an NFT)
- Buy a property (buy NFT shares)
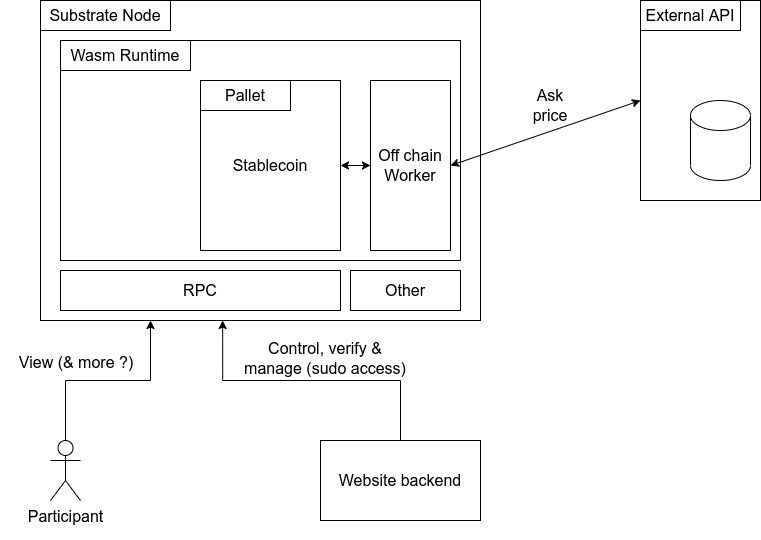
A word about Substrate modules and NFT
In the Substrate Framework pallets (also called modules) are small components that are part of the blockchain core functionalities (i.e. runtime). The pallets are analogous to smart contracts.
The purpose of Substrate is to build specific blockchain architectures for specific use-cases, thus creating domain-specific pallets. We send extrinsics (i.e. transactions) to the pallets.
In our project, we used a blockchain node template provided by Substrate. We then created a pallet to handle the project business logic (mainly create/sell/buy NFTs).
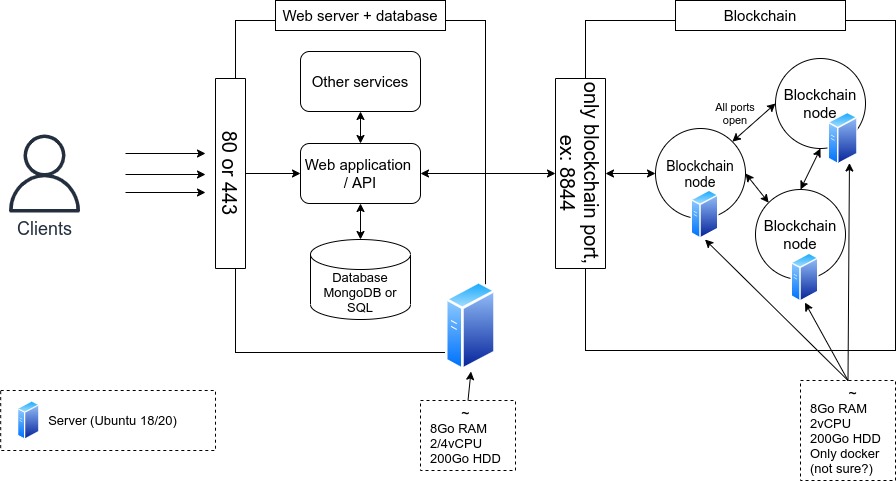
We opt for a basic system architecture for the hackathon with a first server to handle all incoming requests and three servers to host the private blockchain nodes.
Thank you Ziosting for providing us with these machines!

Future works
The hackathon has jump-started the project: created a team & connections, focus the project target, and helped us with sorting out issues and pitfalls.
In future works some key elements are to develop to follow existing regulations :
- KYC: It is required to know the identity of property owners.
It is only by knowing the customer that we can apply current legislation.
The project needs a team member in the legal and notary fields. - Apply privacy by design, secure the blockchain, website, and build a production-ready environment.
- Find venture capitalists, investors, and mentors.
A useful feature of the platform would be to enable stablecoin cryptocurrency. This would ease the transition from fiat money to cryptocurrency. Potential users of the platform necessarily do not have in-depth knowledge of cryptocurrency and tokens in general, thus building a fiat-backed stablecoin can be an advantage.
Hackathon standings
The final hackathon ended with the following standings:
- Blockchain Your Art
- SecureContracts
- Updownstreet
- Stable Chain
References and links
- Proof of Attendance Protocol (POAP): Attendance NFT Link Here.
- Hackathon replay and videos: https://app.meltingspot.io/e/f7946cb9-5390-47e8-a7d5-d531d988a8d9
- Hackathon PoC: https://www.updownstreet.com/



